DC charging benefits
DC chargers are the key to a fast charging infrastructure, allowing electric vehicle drivers to gain a lot of range in a short time. Charge the car in a fast time.
The autonomy of electric vehicles was one of the most feared elements by the drivers of this type of cars. With the increase in the number of electric vehicle owners, one of the main problems today is the charging speed, where the time to recharge the car can be decisive in some situations.
On a practical level, the other change with respect to the experience with a combustion vehicle is in energy charging, where the question of who replaces gas stations arises? We all understand the ease of the new process when it comes to plugging in the car at home, at night, but what about long journeys? What if you don’t have a parking space?
This is where it is necessary to analyze the different types of electric vehicle charging, in this way it is possible to know which one will be able to provide a faster charging service.
- AC chargers: where the charger sends Alternating Current (AC) to the car.
- DC chargers: here, the charger sends direct current (DC) to the vehicle.
Before continuing, it is worth mentioning that the major automotive brands have developed a standard connector that makes 97% of electric vehicles accept both AC and DC charging. The electric vehicle connectors are mechanically prepared to fit both an AC connector and a DC connector. This standard connector is the CCS2 (Combined Charging System 2 or Combo 2).
Electric vehicle charging types: AC and DC
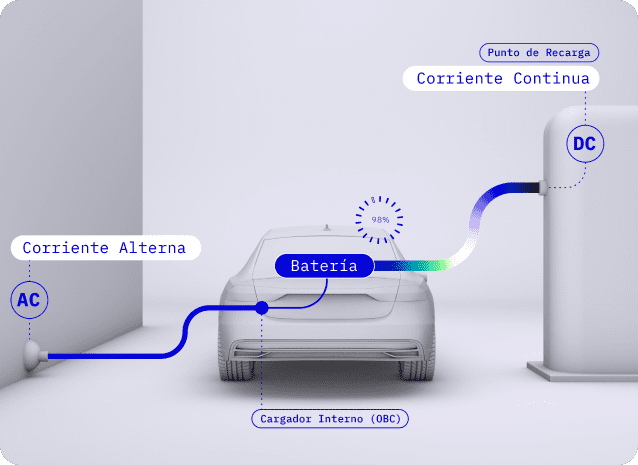
First of all, it must be understood that the electrical system around us always works with AC electricity: the large power transmission lines, the distribution networks to homes and businesses, the sockets where appliances and machines are plugged in.
However, the batteries of electric vehicles run on DC, both to deliver power to the vehicle (discharge) and to power it (charge). Here is the crux of the matter: who transforms the AC electricity from the grid to DC electricity needed by the battery? There are two possibilities, the first would be done by the car itself, and the second would be done externally. This is the fundamental difference between AC and DC chargers.

- AC chargers deliver AC electricity to the vehicle. This, before reaching the battery, must transform it into DC, through the “on-board charger” commonly known as OBC (On Board Charger). The function of the AC charger is not to transform the electricity, but to deliver more power than a conventional plug, to have protections that prevent scares for both the home network and the car, as well as providing intelligence options such as user authentication, use of a control and monitoring app, etc.
- DC chargers deliver DC electricity to the car, ready for use. This energy can go directly to the battery, without passing through any other device. Thus the charger does the conversion, offering many advantages.
Technical details of chargings
AC charging
Currently, AC charging is the most widespread in the market, being very reasonably priced. More than 85% of current charging stations are AC charging stations, both in private garages and in the charging stations that some municipalities make available to citizens. The same ease of installation, for example, in private homes means that its power is limited by the contracted power in the home, which can be around 7kW or 10kW. Contracting more power exclusively for the charger would be an option, but very expensive, since it would be necessary to change the entire electrical connection. The implication is that it is a slow recharge.
- Up to 3.7kW requires 6 to 8 hours of charging, usually used during the night. This type of power is very affordable in private electrical connections.
- Between 7.4 kW and 22kW, the chargers can recharge the vehicle between 3 and 4 hours.
DC Charging
With DC charging the power delivered to the vehicle can be higher: 30, 50, 100, 150, 180kW… even more, with chargers that will need special extra cooling. The maximum is set by the electrical supply. The charging station owner’s goal is to be able to offer the best service for his customers, which means an excellent, queue-free and fast user experience. DC chargers include all this technology inside. A part of power electronics and another part of intelligence and control, so that the managers of the points can control them remotely, give access to users (with contactless cards or key fobs, APPs on the mobile, even soon it will be the car itself that will identify itself to the charger). They are the ideal chargers for these places where the car does not sleep, but is just passing through.
- With a 30KW charging station you can charge up to 200km of autonomy in one hour, which makes them ideal for parking lots of shopping centers or restaurants.
- With a 150 kW charging station, up to 300 km of range can be obtained in less than 20 minutes of charging. These charging solutions are perfect for charging stations and areas where the user cannot wait for a long time.
Alternating current charging is associated with slower charging and longer times; direct current charging offers higher charging power and lower times.
Advantages of DC charging
By outsourcing the AC to DC power transformation function, DC chargers offer two advantages:
The first is that by not having to go through the OBC, a load limiter is removed. The vehicle control systems will always control the power to be injected, but they will do so based on the capacity of the battery, not the capacity of the OBC.
The second is that the spatial boundary disappears. The AC to DC transformer no longer needs to be small and light to fit somewhere in the vehicle. By being able to make it larger, it can be made much more powerful: the more power, the less time it will take to charge.
DC chargers are the key to a fast charging infrastructure that allows electric vehicle drivers to gain a lot of range in a short time. Charge the car in a fast time.
In less than 40 minutes, 80% of many of the most common batteries in today’s vehicles will have been charged. On-the-go charging is gaining more and more ground and is starting to be visualized little by little. That’s where we want to take you with Floox DC fast chargers.